
Flashcards
21/02/2018
Languages on holiday
04/07/2018I
n today's post I would like to shed some light on the language levels used to establish the level of knowledge of a foreign language. Very often people who speak a foreign language do not know what to indicate on their curriculum vitae in the section related to language skills, or have difficulties when they have to self-assess their level of knowledge of a foreign language if they have not obtained any kind of specific certification attesting their language level.
T he instrument allowing us to define the different language levels is the European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR), which was established by the Council of Europe with the aim of defining language levels recognised at the European level. This framework objectively establishes universal levels of language skills acquired and it allows you to create appropriate teaching plans for language teaching.
T he instrument allowing us to define the different language levels is the European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR), which was established by the Council of Europe with the aim of defining language levels recognised at the European level. This framework objectively establishes universal levels of language skills acquired and it allows you to create appropriate teaching plans for language teaching.
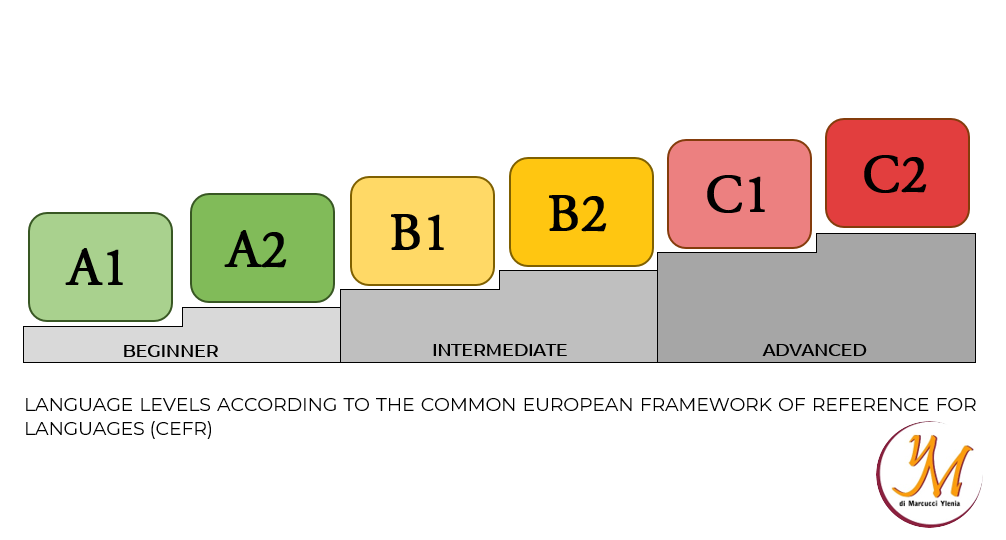
T
he reference framework identifies three broad levels (beginner, intermediate and advanced) which are respectively indicated by the letters A, B and C. These levels are in turn divided into six levels of proficiency (A1, A2, B1, B2, C1 and C2) and three intermediate levels (A2+, B1+, B2+). We can see that A1 corresponds to the beginner level while C2 corresponds to the more advanced level.
Let's take a closer look at the skills required for each level:
I n order to assess your language level objectively, you should take an exam at a certified language body that can issue a language certificate after having objectively established your language skills. This will take into account the four main language skills that are assessed in any language exam, i.e.:
I hope that this post has helped you to better understand how language levels are defined and that you are willing to improve your language level, whatever it is!
Let's take a closer look at the skills required for each level:
- Beginner level (A1, A2): users with basic knowledge of the foreign language can understand simple everyday expressions, can introduce themselves and have a short conversation on familiar topics with a person who speaks slowly and uses a simple vocabulary.
- Intermediate level (B1, B2): users with an intermediate level are able to take part in a more complex conversation on topics of interest and of which they have general knowledge. They can easily understand and make themselves understood in the workplace or during a trip abroad and they can have a conversation on more technical topics on which they have more extensive general knowledge. They are also able to express their ideas and opinions on more abstract topics and can use different language registers depending on the situation and the person they are talking with.
- Advanced level (C1, C2): users with an advanced level of proficiency in the foreign language can understand anything they hear or read, even on unfamiliar and complex subjects. They can express themselves correctly both orally and in writing, correctly identifying the various nuances of the language, including abstract language, and they can have a conversation on subjects involving a high level of complexity, using a style which is appropriate to the context and being able to use idioms and figures of speech. Users with this level of command will master the language to a degree which is comparable to that of a native speaker, although it is difficult to think that they will be able to speak spontaneously on any subject, especially technical ones, without any preparation - since perhaps none of us would be able to do that even in our mother tongue.
How to assess the level of proficiency in the foreign language?
I n order to assess your language level objectively, you should take an exam at a certified language body that can issue a language certificate after having objectively established your language skills. This will take into account the four main language skills that are assessed in any language exam, i.e.:
- Reading (ability to understand a written text)
- Listening (ability to understand an oral text without written support)
- Writing (ability to write a text in the foreign language)
- Speaking (ability to express oneself orally on a given topic)
I hope that this post has helped you to better understand how language levels are defined and that you are willing to improve your language level, whatever it is!









